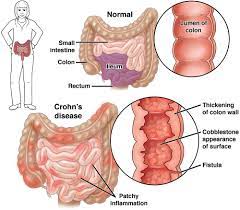
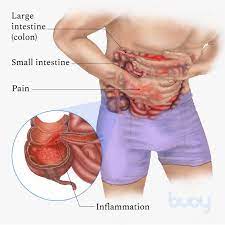
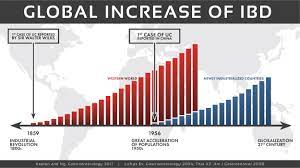
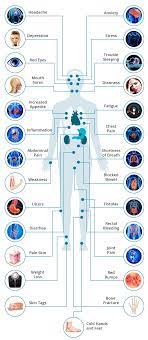
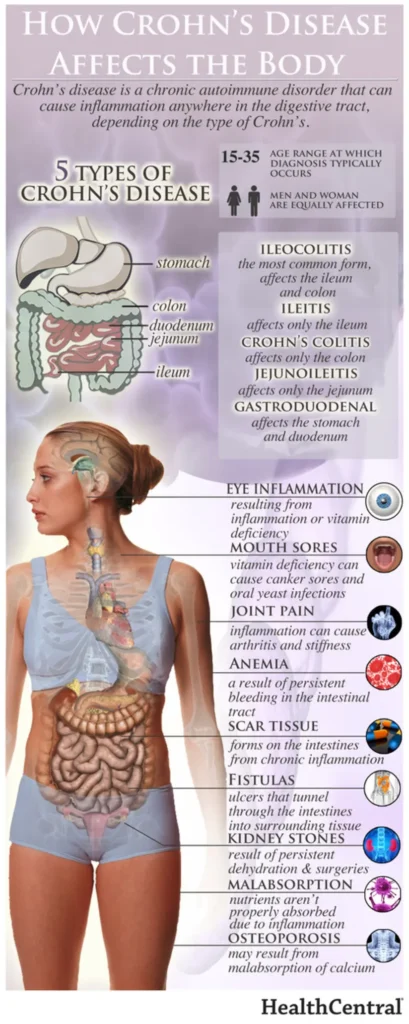
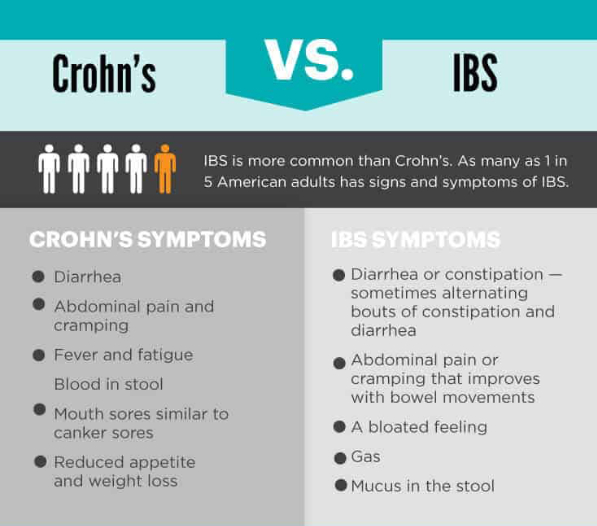
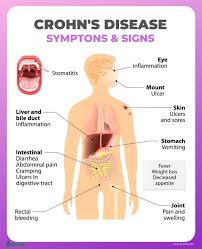
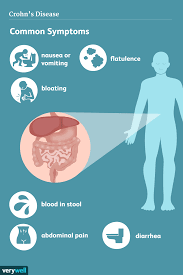
Hydrogen generated by Si-based agent attenuates inflammation in ulcerative colitis mouse model

Researchers designed a silicon-based agent that successfully generated hydrogen continuously in the mouse gastrointestinal tract in an ulcerative colitis (UC) model. The hydrogen served as an antioxidant that could eliminate the reactive oxygen species shown to induce the chronic inflammation responsible for the damage and symptoms caused by UC. Mice given the agent had reduced hemorrhage, inflammation, and hyperexcitability in the brain area associated with visceral pain and discomfort. These results may help with the development of a novel treatment for UC.