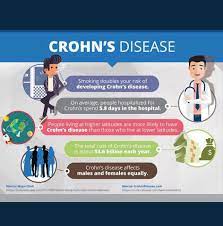
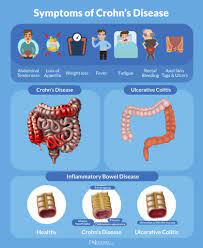
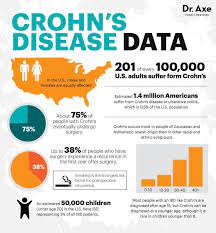
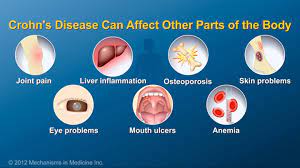
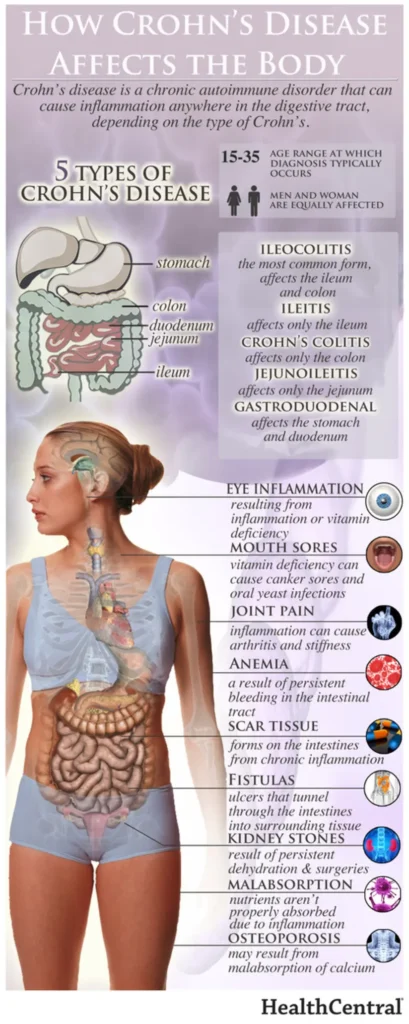
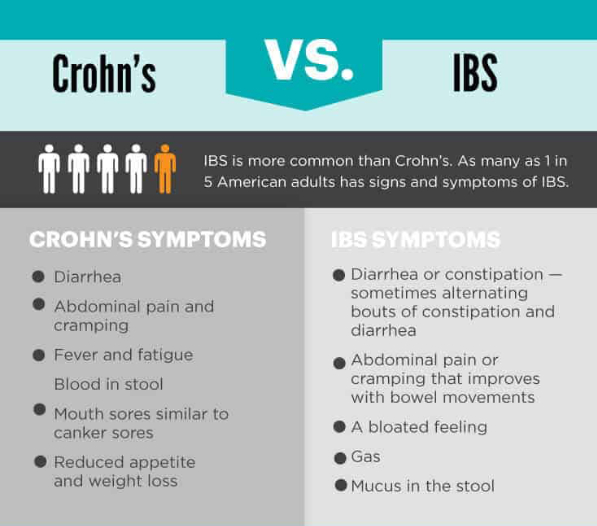
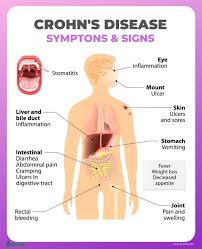
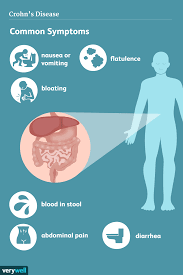
Potential new therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases such as lupus and sepsis

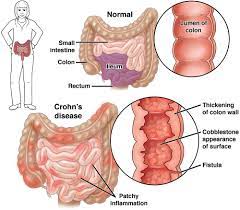
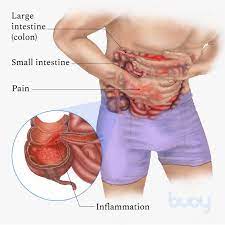
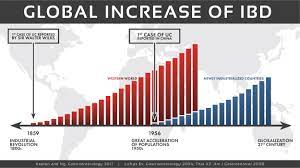
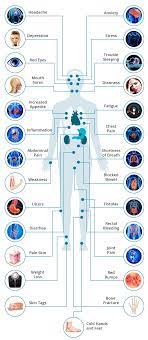
Scientists have made an important breakthrough in understanding what goes wrong in our bodies during the progression of inflammatory diseases and — in doing so — unearthed a potential new therapeutic target. The scientists have found that an enzyme called fumarate hydratase is repressed in macrophages, a frontline inflammatory cell type implicated in a range of diseases including lupus, arthritis, sepsis and COVID-19.