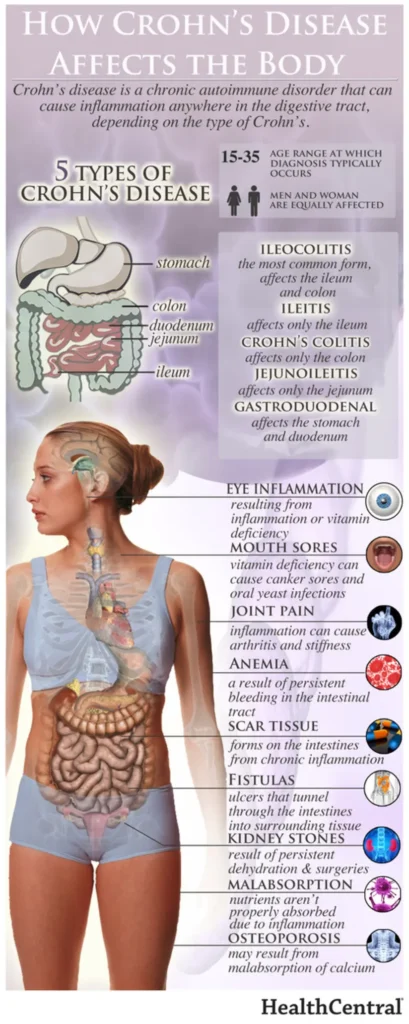
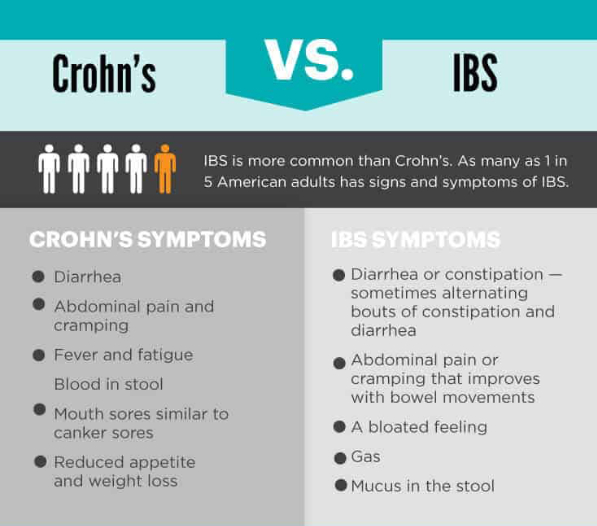
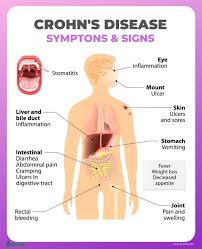
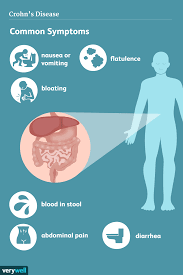
Food additive carrageenan (E 407) could disrupt the intestinal barrier and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, study finds

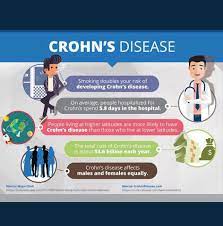
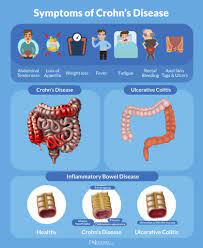
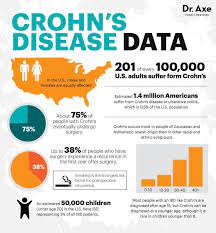
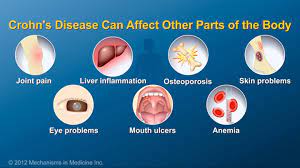
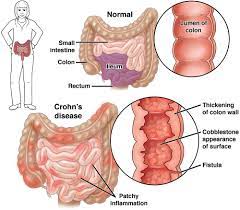
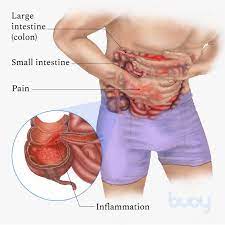
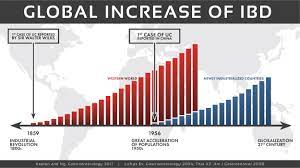
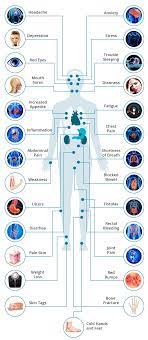
The food additive carrageenan (E 407) can be responsible for the development of chronic inflammatory bowel disease, ulcers, and increased blood sugar levels in animals. Researchers have now investigated the effects of carrageenan on the human intestine and sugar metabolism. They found increased permeability of the small intestine, most likely due to intestinal inflammation.