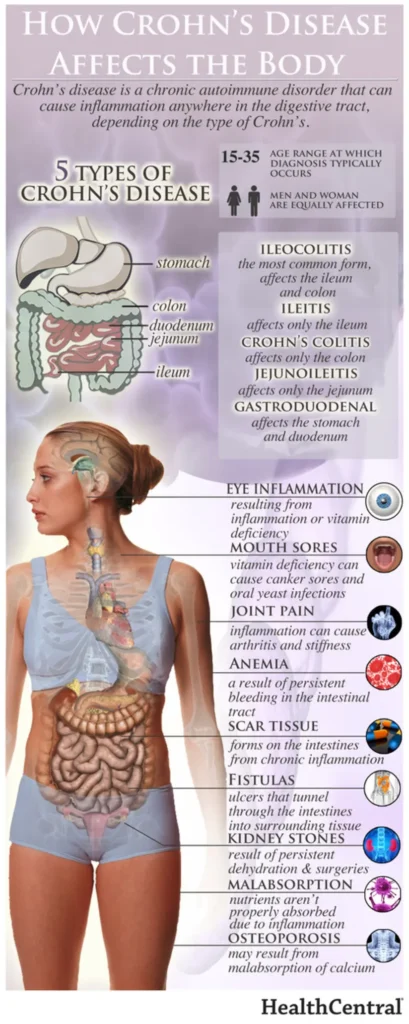
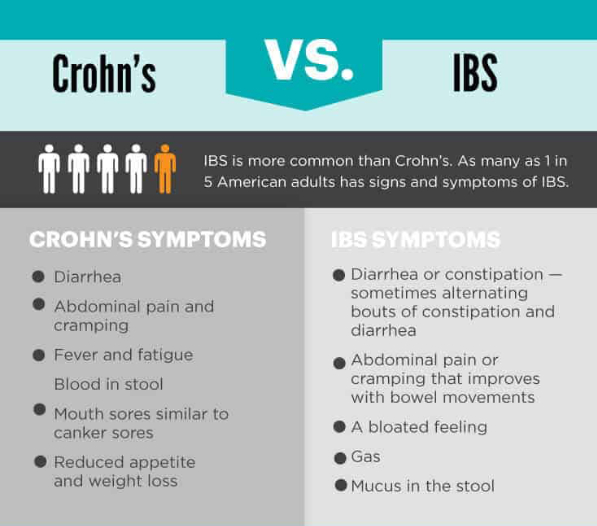
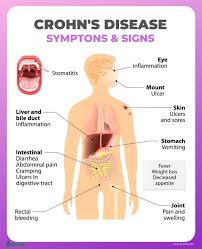
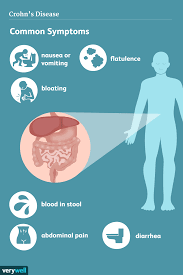
Mechanisms of Action of Exclusive Enteral Nutrition and Other Nutritional Therapies in Crohn’s Disease

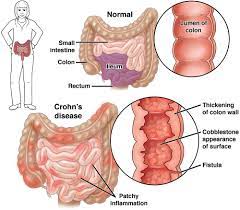
Figure 1. Proposed mechanisms of action of EEN in Crohn’s disease (CD). Transmural inflammation and stenosis in CD lead to increased mechanical stress (MS) in the inflamed tissue and the segment proximal to inflammation. Both the inflammatory process and MS may induce proinflammatory molecules (i.e., COX-2), cytokines and chemokines (i.e., IL-6, IL-8, osteopontin), and pain mediators (i.e…